Cardioselective Beta Blockers Mnemonic: The Ultimate Guide To Mastering Beta Blockers
Let’s talk about cardioselective beta blockers mnemonic, a game-changer in the world of pharmacology that every med student and healthcare professional should know like the back of their hand. If you’ve ever found yourself scratching your head trying to remember which beta blockers are cardioselective and why they matter, you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about these drugs in a way that’s easy to digest and remember.
Now, here’s the deal—beta blockers are a big deal in medicine, but not all of them are created equal. Cardioselective beta blockers are a specific group that targets the heart without messing too much with other parts of your body. This makes them safer for certain patients and more effective for specific conditions. Understanding their nuances can mean the difference between a successful treatment plan and one that falls flat.
Whether you’re cramming for exams, prepping for clinical rotations, or just brushing up on your pharmacology knowledge, mastering cardioselective beta blockers is essential. And guess what? We’ve got a mnemonic that’ll stick in your brain like glue. So grab a cup of coffee, get comfy, and let’s dive into the world of cardioselective beta blockers.
- Archie Manning Eine Legende Familie Amp Footballikone
- Iamxs Meisterwerk Eine Tiefgrndige Analyse Von Bernadette Jetzt Neu
Table of Contents
- What Are Cardioselective Beta Blockers?
- A Brief History of Beta Blockers
- Cardioselective vs Non-Selective Beta Blockers
- The Ultimate Mnemonic for Cardioselective Beta Blockers
- How Do Cardioselective Beta Blockers Work?
- Clinical Uses of Cardioselective Beta Blockers
- Side Effects to Watch Out For
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Comparison with Other Antihypertensive Drugs
- Tips for Remembering Cardioselective Beta Blockers
- Wrapping It All Up
What Are Cardioselective Beta Blockers?
Cardioselective beta blockers are a subclass of beta blockers that primarily target beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart. Unlike their non-selective counterparts, these drugs spare beta-2 receptors in the lungs and other tissues, reducing the risk of side effects like bronchoconstriction. This selectivity makes them ideal for managing conditions like hypertension, angina, and heart failure.
Think of cardioselective beta blockers as the "gentle giants" of the beta blocker family. They get the job done without causing unnecessary chaos in other parts of the body. Some common examples include metoprolol, atenolol, and bisoprolol. Sound familiar? If not, don’t worry—we’ll cover these in more detail later.
A Brief History of Beta Blockers
The discovery of beta blockers revolutionized modern medicine. James W. Black, a Scottish pharmacologist, developed the first beta blocker, propranolol, in the early 1960s. This groundbreaking drug paved the way for the development of more selective beta blockers, including the cardioselective ones we use today.
- Bryton Myler Ninja Kidz Tv Star Sein Aufstieg Amp Erfolgsgeheimnis
- Die Manningdynastie Eine Footballfamilie Schreibt Geschichte
Over the decades, researchers have refined beta blockers to target specific receptors, improving their safety and efficacy. Cardioselective beta blockers emerged as a response to the need for drugs that could treat cardiovascular conditions without compromising respiratory health. Pretty cool, right?
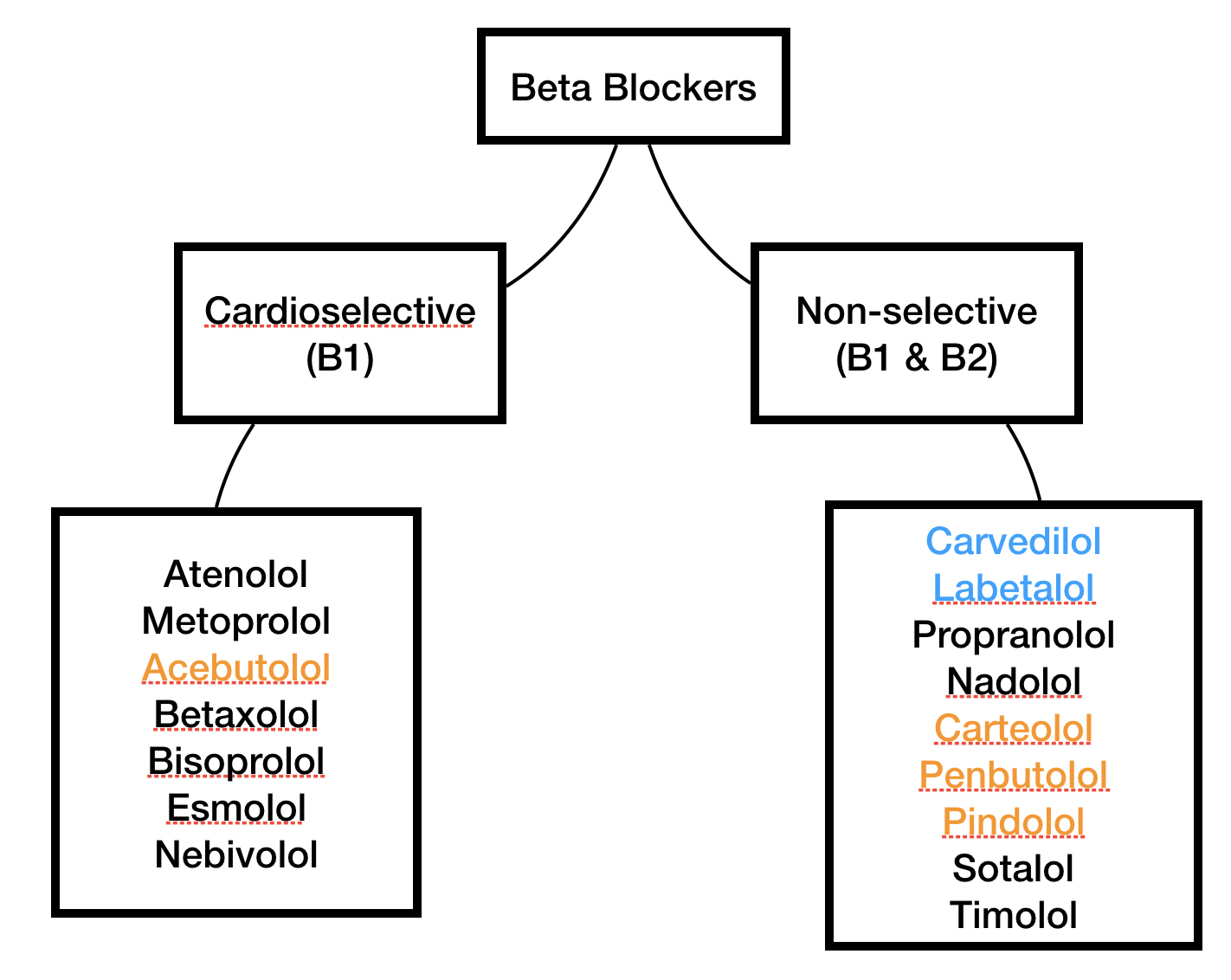
Cardioselective vs Non-Selective Beta Blockers
Key Differences
So, what’s the big difference between cardioselective and non-selective beta blockers? It all comes down to receptor specificity. Non-selective beta blockers, like propranolol, block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors, which can lead to unwanted side effects like wheezing and bronchospasm. Cardioselective beta blockers, on the other hand, focus their attention on beta-1 receptors in the heart, minimizing effects on beta-2 receptors elsewhere.
Here’s a quick rundown of the main differences:
- Cardioselective Beta Blockers: Primarily target beta-1 receptors; safer for respiratory patients.
- Non-Selective Beta Blockers: Block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors; higher risk of respiratory side effects.
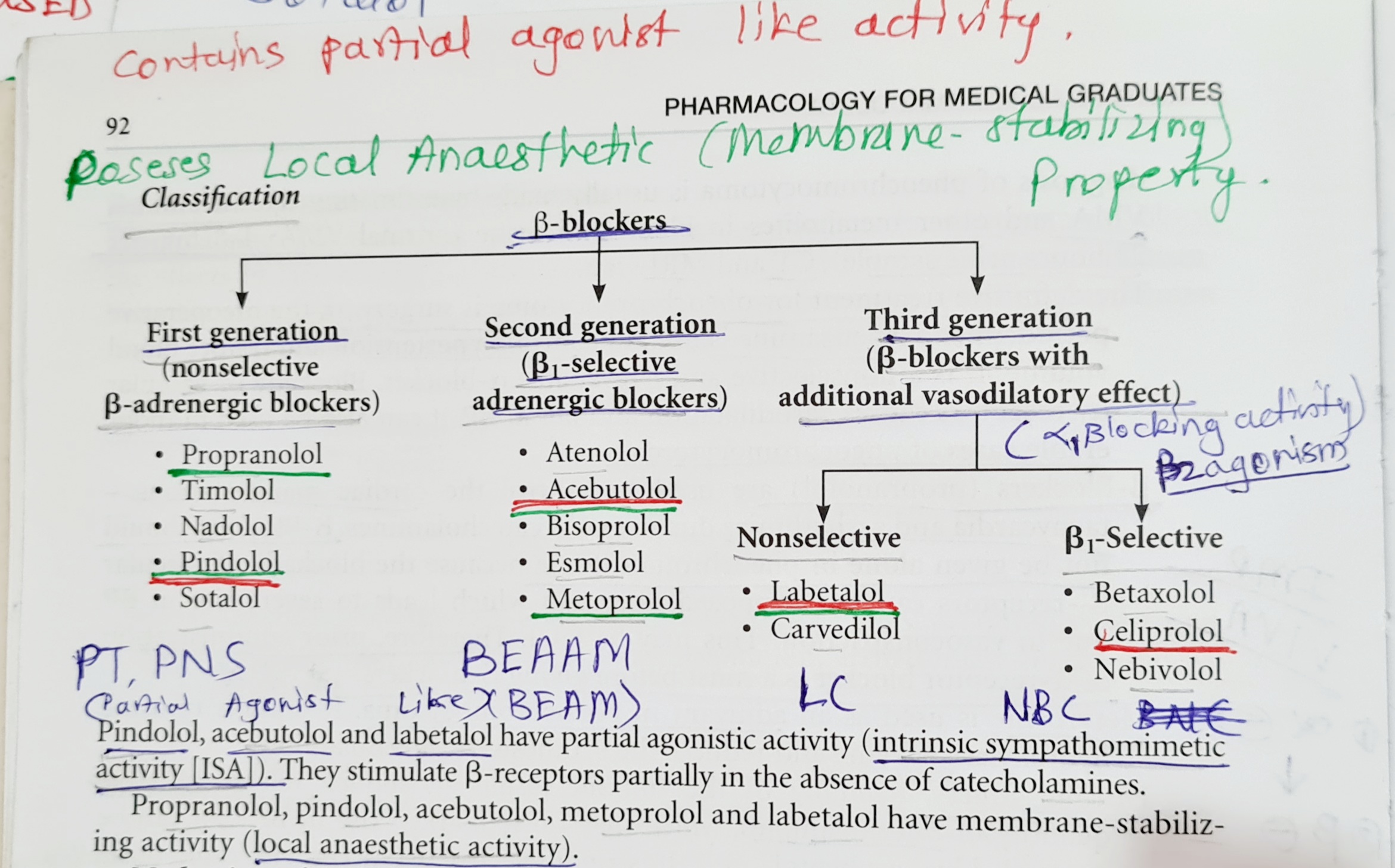
The Ultimate Mnemonic for Cardioselective Beta Blockers
Now for the fun part—the mnemonic! Remembering the names of cardioselective beta blockers can be a challenge, but with the right trick, it’s a piece of cake. Here’s a mnemonic to help you out:
MABE: Metoprolol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Esmolol.
Think of it as "MABE," the friendly pharmacist who always has your back when it comes to cardioselective beta blockers. Easy, right? Now you’ll never forget the key players in this category.
How Do Cardioselective Beta Blockers Work?
The mechanism of action of cardioselective beta blockers is all about blocking beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart. By doing so, these drugs reduce the heart’s workload, lower blood pressure, and decrease oxygen demand. This makes them incredibly useful for managing conditions like:
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias
Imagine your heart as a car engine that’s running too fast. Cardioselective beta blockers are like the brakes that slow it down, preventing it from overheating and breaking down.
Clinical Uses of Cardioselective Beta Blockers
Conditions Treated
Cardioselective beta blockers are versatile drugs with a wide range of clinical applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Hypertension: Lowering blood pressure without causing respiratory issues.
- Angina: Reducing the heart’s oxygen demand to relieve chest pain.
- Heart Failure: Improving cardiac function and reducing mortality.
- Arrhythmias: Slowing down the heart rate to manage irregular rhythms.
Each of these conditions benefits from the heart-focused action of cardioselective beta blockers, making them a go-to choice for many healthcare providers.
Side Effects to Watch Out For
While cardioselective beta blockers are generally well-tolerated, they’re not without side effects. Some common ones include:
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
It’s important to monitor patients closely, especially when starting or adjusting doses. Always remember the golden rule: Start low and go slow to minimize side effects.
Contraindications and Precautions
Not everyone is a good candidate for cardioselective beta blockers. Here are some contraindications and precautions to keep in mind:
- Severe Bradycardia: Avoid in patients with very slow heart rates.
- Heart Block: Use with caution in patients with conduction abnormalities.
- Asthma or COPD: While cardioselective beta blockers are safer than non-selective ones, they should still be used cautiously in respiratory patients.
Always review a patient’s medical history before prescribing these drugs to ensure their safety.
Comparison with Other Antihypertensive Drugs
Why Choose Cardioselective Beta Blockers?
When it comes to treating hypertension, cardioselective beta blockers aren’t the only game in town. Other antihypertensive drugs, like ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers, also play a role. So, why choose cardioselective beta blockers?
For one, they’re particularly effective in patients with comorbid conditions like angina or heart failure. Additionally, their cardioselective nature makes them a safer option for patients with respiratory issues. It’s all about finding the right drug for the right patient.
Tips for Remembering Cardioselective Beta Blockers
Remembering the names of cardioselective beta blockers doesn’t have to be a chore. Here are a few tips to help you ace this topic:
- Use the MABE mnemonic: Metoprolol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Esmolol.
- Associate each drug with its key features: Metoprolol for metabolism, Atenolol for angina, Bisoprolol for balance, Esmolol for emergency use.
- Create flashcards or mind maps to reinforce your learning.
With a little practice, you’ll have these drugs memorized in no time.
Wrapping It All Up
Cardioselective beta blockers are powerful tools in the pharmacological arsenal, and mastering them is essential for anyone in the healthcare field. From their mechanism of action to their clinical uses and potential side effects, understanding these drugs inside and out will make you a better clinician.
So, what’s next? Take a moment to reflect on what you’ve learned and apply it to your studies or practice. Share this article with your colleagues or classmates, and let’s spread the knowledge together. And remember, if you ever need a refresher, the MABE mnemonic’s got your back!
Got questions or feedback? Drop a comment below or share this article with someone who could benefit from it. Let’s keep the conversation going and make pharmacology a little less intimidating for everyone!
- Filmy4wap Co Kostenlose Filme Die Risiken Des Piratendownloads
- Filmy4web Co Kostenlose Filme Legal Sicher Ein Berblick

Cardioselective Beta Blockers Mnemonics, MOA & Uses
Classification Of Beta Blockers And The Mnemonics Bet vrogue.co
Classification Of Beta Blockers And The Mnemonics Bet vrogue.co